22 May 2020
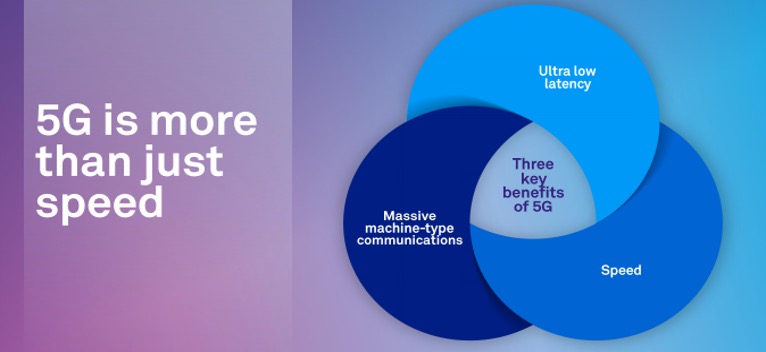
5G has significantly increased the speed and responsiveness of wireless networks and expand them to enable hundreds of thousands of connections. 5G offers greater capacity, higher data rates and much lower latency, and it will support further innovations such as the internet of things (IoT) and network slicing, creating a smarter, more connected world.
Key Benefits of 5G
Connected vehicles
With 5G comes unprecedented speed and connectivity the kind needed to make autonomous, or self-driving, cars a reality. 5G networks have what it takes to allow faster than ever communication and data processing between vehicles, networks, infrastructure and even pedestrians. In other words, 5G networks will facilitate communication between everything on the road from lampposts to gas stations in the interest of safety and traffic management.
Smartphones
The main advantage of 5G over 4G for users is better coverage, i.e., signals hit previously hard to reach places with connection guaranteed as part of service plans. What's more, subscribers have finally got the extraordinary quality they expect on their devices, with downloads predicted to have no perceptible delay.
Streaming and Entertainment
5G offers a striking advantage over previous technologies, with virtually unlimited capacity and short lag times. In addition to better quality and considerably faster streaming, 5G promises revolutionary immersive experiences, including multisensory digital content thanks to the increased capacity that will support technologies like virtual reality, augmented reality and 3D.
Implementing Technologies
5G promises a range of use cases including IoT, industrial IoT, smart cities and transportation and real-time video but guaranteeing the performance of these new services and applications will require flawless service assurance solutions. And to support these various industry use cases, Telstra is transforming its network architecture.
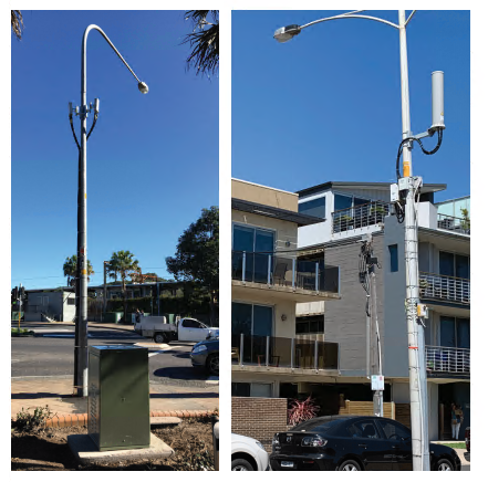
Macrocells, small cells and dedicated in building systems
5G networks are designed to work in conjunction with 4G networks using a range of macrocells, small cells and dedicated in-building systems.
Small cells will be a feature of 5G networks and will evolve to include the use of millimetre wave (mmWave) frequencies. Small cells are mini base stations designed for very localized coverage typically from 10 meters to a few hundred metres providing infill for the more extensive macro network. Small cells will be essential for 5G networks.

5G Network
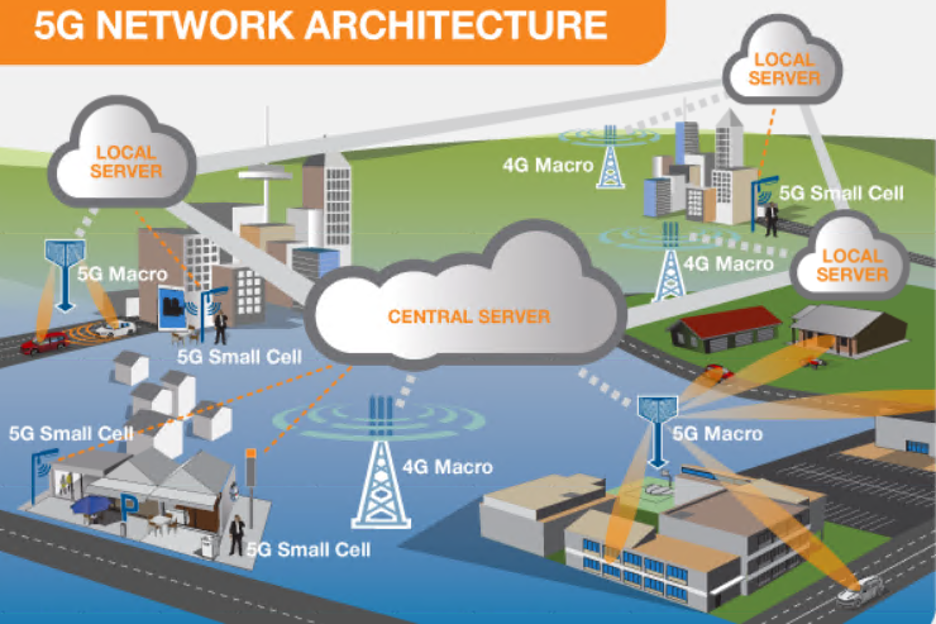
The network architecture illustrates 5G and 4G working together, with central and local servers providing faster content to users and low latency applications.
Components of Mobile Network
A mobile network has two main components, the Radio Access Network and the Core Network.
The Radio Access Network
It consists of various types of facilities, including small cells, towers, masts and dedicated in-building and home systems that connect mobile users and wireless devices to the main core network.
Small cells will be a significant feature of 5G networks, particularly at the new millimetre wave (mmWave) frequencies where the connection range is short. To provide a continuous connection, small cells will be distributed in clusters depending on where users require a connection which will complement the macro network that provides wide-area coverage.
5G Macro Cells will use MIMO (multiple inputs, multiple outputs) antennas that have various elements or connections to send and receive more data simultaneously. The benefit to users is that more people can simultaneously connect to the network and maintain high throughput. Where MIMO antennas use vast numbers of antenna elements, they are often referred to as 'massive MIMO'; however, the physical size is similar to existing 3G and 4G base station antennas.
The Core Network
It is the mobile exchange and data network that manages all of the mobile voice, data and internet connections. For 5G, the core network is being redesigned to better integrate with the internet and cloud-based services and includes distributed servers across the network, improving response times (reducing latency).
Many of the advanced features of 5G, including network function virtualization and network slicing for different applications and services, will be managed in the core. The following illustration shows examples of local cloud servers providing faster content to users (movie streaming) and low latency applications for vehicle collision avoidance systems.
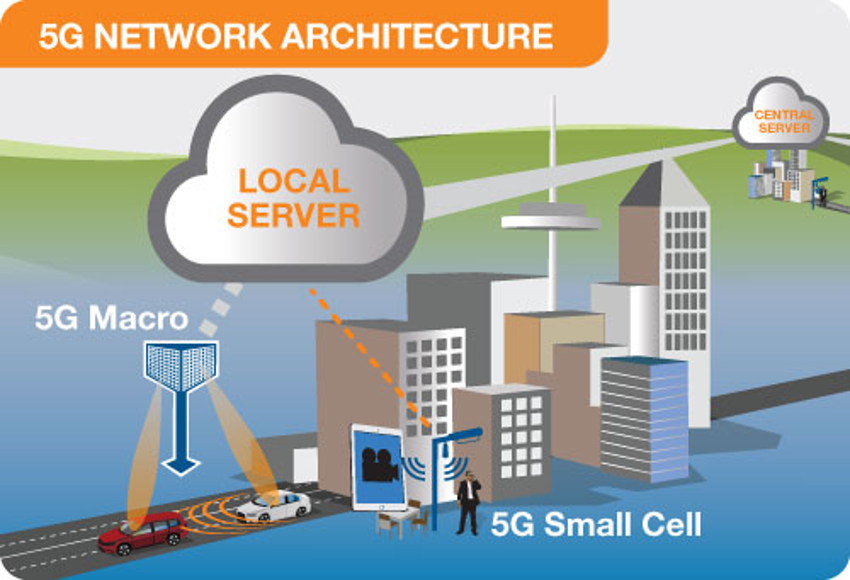
Example of a local server in a 5G network providing faster connection and lower response times
Network Slicing enables a smart way to segment the network for a particular industry, business or application. For example, emergency services could operate on a network slice independently from other users.
Why network slicing?
Network slicing enables the most economical model to provide service differentiation and meeting end-user SLAs. The overall opportunity with network slicing is that it opens up for new types of service offerings and support different enterprise business models, flexibly with a high service deployment velocity.
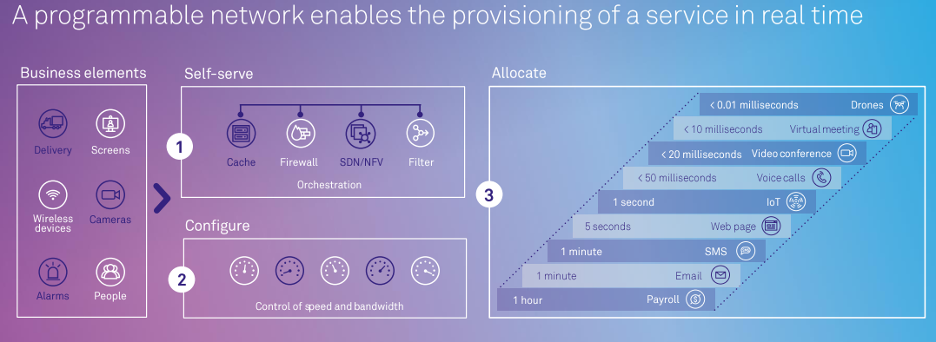
End-to-end network slicing is the defining 5G feature. 5G network slicing splits resources into logical or virtual networks "slices" to address use cases with distinct characteristics and service level agreement (SLA) requirements.
Network Function Virtualization (NVF)
It is the ability to instantiate network functions in real-time at any desired location within the operator's cloud platform. Network functions that used to run on dedicated hardware, for example, a firewall and encryption at business premises can now operate on software on a virtual machine. NVF is crucial to enable speed efficiency and agility to support new business applications and is an essential technology for a 5G ready core.
Business Use Cases
Automotive Industry
Vehicle communication has been investigated long before 5G. It is possible to perform automatic driving via in-car sensors like camera, radar, lidar. However, 5G's design is targeted to offer stringent performance, such as ultra-low latency and ultra-high reliability that will bring vehicle communication to the next level, e.g. from assisted-driving to cooperative autonomous driving.
Vehicle communication that relies on a network requires a wide coverage range, e.g. along the highway, in rural or in the urban area. Hence, the operator will play a vital role in the ecosystem of the automotive industry. Due to security concern, automotive companies may deploy their private cloud environment to host automotive applications. To cope with performance requirements, it is essential for a vertical customer to seamlessly integrate its resources as well as services together with an operator's territory.
Industry
Due to the excellent progress of IoT, industrial automation, cloud technology, etc., the manufacturing industry is also undergoing the digital transformation process. Being different from the above mentioned automotive industry, players from manufacturing industry usually have more diverse business roles in its ecosystem. On one side, they could be providers for external customers in terms of mechanical components, technical solutions, etc.. On the other hand, they could be the users of their solution, e.g. digitizing their plants. Especially for cases like control of industrial machines, communication is usually limited within the factory campus. Manufacturing industry players may well be using private networks (unlicensed or granted usage of the licensed spectrum) tougher with their cloud resources. The business scope for such manufacturing industry is very international. For tier-one players, the number of plants may be in the order of two to three digits and spread in different countries and even continents. Therefore, global network slicing operation is essential for such use case. Moreover, global network slicing concept will also bring added-value for the vertical customer in terms of business development, because under one unified platform could shield the complexity of business negotiation among different administrative domains.
For business
5G and IoT will provide a wealth of data allowing them to gain insights into their operations like never before. Companies will operate and make critical decisions driven by data, innovate in agriculture, smart farms and manufacturing, paving the way for cost savings, better customer experience and long term growth.
3 Strategies to Reduce Telecom Cost




